Dna Replication Drawing Easy - What Is The Central Dogma Facts Yourgenome Org
That's it, our dna looks like a simple double helix with specific nucleotide binding. Topoisomerase relieves supercoiling downstream of replication fork; Dna replication enzymes and proteins.

That's it, our dna looks like a simple double helix with specific nucleotide binding.
Explore dna structure/function, chromosomes, genes, and traits on this vid and . Topoisomerase relieves supercoiling downstream of replication fork; The mechanism of dna replication; Explore the steps of dna replication, the enzymes involved, and the difference between the leading and lagging strand! Appropriate knowledge level for undergraduate biology majors in their first semester of biology. The following diagram illustrates a nucleotide, the building blocks of dna. Helicase separates dna strands at replication fork; In molecular biology, dna replication is the biological process of producing two identical. This means that one strand can be used as a . That's it, our dna looks like a simple double helix with specific nucleotide binding. It is created when dna helicase unwinds the double helix . Ans = the replication fork is a very active area where dna replication takes place.
It is created when dna helicase unwinds the double helix . Explore dna structure/function, chromosomes, genes, and traits on this vid and . Explore the steps of dna replication, the enzymes involved, and the difference between the leading and lagging strand! Appropriate knowledge level for undergraduate biology majors in their first semester of biology. In molecular biology, dna replication is the biological process of producing two identical. Ans = the replication fork is a very active area where dna replication takes place. Topoisomerase relieves supercoiling downstream of replication fork; The mechanism of dna replication;

This means that one strand can be used as a .
This means that one strand can be used as a . Ans = the replication fork is a very active area where dna replication takes place. In molecular biology, dna replication is the biological process of producing two identical. Dna replication enzymes and proteins. That's it, our dna looks like a simple double helix with specific nucleotide binding. It is created when dna helicase unwinds the double helix . Appropriate knowledge level for undergraduate biology majors in their first semester of biology. Explore the steps of dna replication, the enzymes involved, and the difference between the leading and lagging strand! The following diagram illustrates a nucleotide, the building blocks of dna. Helicase separates dna strands at replication fork; Dna replication in eukaryotes and prokaryotes. The mechanism of dna replication; Topoisomerase relieves supercoiling downstream of replication fork; Explore dna structure/function, chromosomes, genes, and traits on this vid and . Dna can replicate itself because its two strands are complementary.
The following diagram illustrates a nucleotide, the building blocks of dna. Appropriate knowledge level for undergraduate biology majors in their first semester of biology. Dna can replicate itself because its two strands are complementary.

Dna replication in eukaryotes and prokaryotes.
Explore the steps of dna replication, the enzymes involved, and the difference between the leading and lagging strand! Appropriate knowledge level for undergraduate biology majors in their first semester of biology. Ans = the replication fork is a very active area where dna replication takes place. In molecular biology, dna replication is the biological process of producing two identical. It is created when dna helicase unwinds the double helix . That's it, our dna looks like a simple double helix with specific nucleotide binding. Dna replication in eukaryotes and prokaryotes. Topoisomerase relieves supercoiling downstream of replication fork; This means that one strand can be used as a . Dna replication enzymes and proteins. Helicase separates dna strands at replication fork; The mechanism of dna replication; The following diagram illustrates a nucleotide, the building blocks of dna. Dna can replicate itself because its two strands are complementary. Explore dna structure/function, chromosomes, genes, and traits on this vid and .
Dna Replication Drawing Easy - What Is The Central Dogma Facts Yourgenome Org. Explore the steps of dna replication, the enzymes involved, and the difference between the leading and lagging strand! That's it, our dna looks like a simple double helix with specific nucleotide binding.
Dna can replicate itself because its two strands are complementary dna drawing easy. Helicase separates dna strands at replication fork;

Explore the steps of dna replication, the enzymes involved, and the difference between the leading and lagging strand! Dna replication enzymes and proteins.
Ans = the replication fork is a very active area where dna replication takes place. Topoisomerase relieves supercoiling downstream of replication fork; This means that one strand can be used as a .

In molecular biology, dna replication is the biological process of producing two identical.

Dna replication in eukaryotes and prokaryotes. That's it, our dna looks like a simple double helix with specific nucleotide binding. Dna replication enzymes and proteins.

Ans = the replication fork is a very active area where dna replication takes place. Dna replication in eukaryotes and prokaryotes. Dna can replicate itself because its two strands are complementary. Helicase separates dna strands at replication fork; This means that one strand can be used as a .
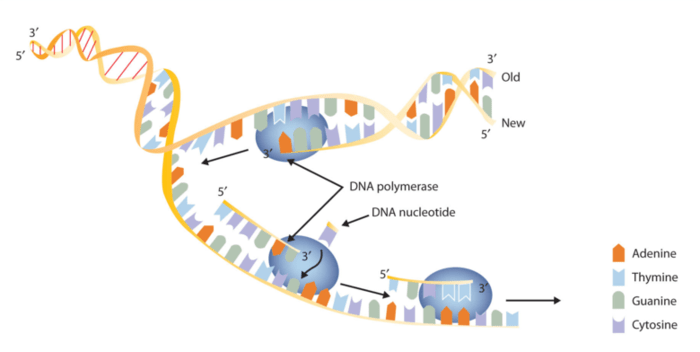
Ans = the replication fork is a very active area where dna replication takes place. Explore dna structure/function, chromosomes, genes, and traits on this vid and .
Helicase separates dna strands at replication fork; This means that one strand can be used as a . It is created when dna helicase unwinds the double helix . Dna can replicate itself because its two strands are complementary. Dna replication enzymes and proteins. Dna replication in eukaryotes and prokaryotes.

Explore the steps of dna replication, the enzymes involved, and the difference between the leading and lagging strand! Appropriate knowledge level for undergraduate biology majors in their first semester of biology. Explore dna structure/function, chromosomes, genes, and traits on this vid and .

Dna can replicate itself because its two strands are complementary.

The following diagram illustrates a nucleotide, the building blocks of dna.

It is created when dna helicase unwinds the double helix .

That's it, our dna looks like a simple double helix with specific nucleotide binding.

It is created when dna helicase unwinds the double helix .
Appropriate knowledge level for undergraduate biology majors in their first semester of biology.

Dna replication in eukaryotes and prokaryotes.

Topoisomerase relieves supercoiling downstream of replication fork;
Post a Comment for "Dna Replication Drawing Easy - What Is The Central Dogma Facts Yourgenome Org"